Introduction
Managing databases efficiently is essential in today's software development industry. However with some IDEs (Integrated Development Environment) tools like IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate, you can integrate and manage your data sources without bothering of installing external database management softwares. From this tutorial you'll be aware on how to configure a new Database/Datasource in IntelliJ IDEA IDE.
While having a built-in data source configured in IntelliJ IDEA is not only simplifies development, but also it saves the valuable time while coding where developers can focus on coding rather than switching between platforms.
So, let’s explore the process of configuring a new data source in IntelliJ IDEA. Moving foreword, we’ll be specifically focussing on setting up a data source for MySQL. However, please note that the steps involved are quite similar for other database types, making it easy to adapt this process to suit your needs. By following this example, you’ll gain a clear understanding of the configuration workflow, ensuring a smooth setup for any supported database system.
How to Configure a New Data Source in IntelliJ IDEA
Open IntelliJ IDEA on your PC or laptop. Ensure that you’re using the latest version to access advanced features available in IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate.
2. Access the Database Tab
- Navigate to the Database tab, typically located in the right-hand corner of the IDE.
- If the Database tab isn’t visible, you can enable it by going to View > Tool Windows > Database.
3. Database Verification
- Before configuring, please ensure that the database you want to connect to is already created. For example, let’s assume a database named supermarket.
- You can ensure the database availability by using following SQL commands.
SHOW DATABASES;- Use this
commandto ensure whether the desired database (e.g.,supermarket) exists on the server. - Example Output:
USE supermarket;- Switch to the active database to
supermarket to ensure that you're working within the intended database for queries or operations. - Example Usage:
- Switch to the active database to
SHOW TABLES;- To view and verify the tables within the selected database database and provides an overview of its structure.
- Example Output:
4. Add a New Data Source
- Click on the plus (+) icon in the Database tab.
- Select Data Source -> MySQL from the dropdown menu.
- You may need to provide the following details in the popup screen:
- Host: If you're using a local DB so it's localhost, otherwise it's your database server’s IP address.
- Port: Please define your Database port here. For MySQL, the default port is 3306.
- Database Name: Enter the name of your database (e.g., supermarket).
- User: Please define your MySQL username here by default you may have a root user.
- Password: Your MySQL Database user password.
- Then please click on Test Connection button to verify the details. If the connection is successful, a green checkmark will appear indicating the successful connection as mentioned below.
6. Save the Configuration
- Once the connection is verified, click Apply and then OK.
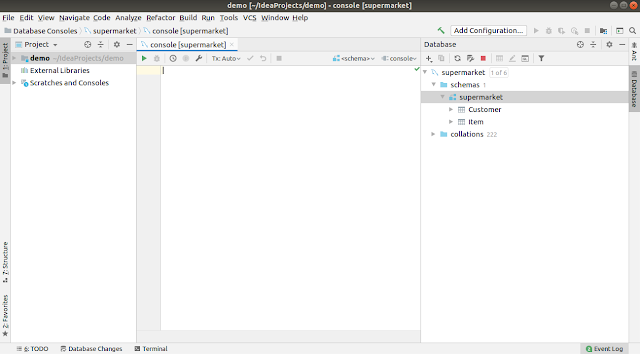
- Your database will now appear in the Database tab.
1 of 6). Hover over this label to reveal a tooltip showing the connection status. If the tooltip displays "0 connections", it means no active connections have been established with the data source yet.8. Select the Schema
- Locate your newly added data source in the Database tab.
- Click on the schema name (e.g.,
supermarket) to view its tables, procedures, and other details.
9. Now you have successfully completed the configuration. Your data source is now set up and ready to use.
Benefits of Using IntelliJ IDEA for Database Management
- Enhanced Productivity: Query and manage data directly within the IDE.
- Integrated Tools: Features like SQL code formatting, syntax validation, and query history improve accuracy and efficiency.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Easily switch between different database systems such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server.













0 Comments